Post-editing
With the development of machine translation (MT), including AI translation, there is a growing demand for “post-editing,” or the reworking of AI translation results. Unlike previous translation methods, which involved translating from scratch, this new method involves revising the results of MT.
Post-editing, which has rapidly developed in recent years, is the process of improving the accuracy of translations generated by MT, including AI translation, by a human editor who revises the text.
More and more companies are adopting MT and post-editing to improve cost performance, with the idea that it will be more productive than human translation.
In addition, post-editing is often chosen as a compromise when there are concerns about the quality of machine-translated translation results, or when it is difficult to hire a translator due to delivery time or cost.
■Difference between Post-editing and Translation
The main difference is that with post-editing a human editor corrects machine translations, whereas with human translation, translations are done by a human from the very beginning.
With post-editing, the human editor checks the MT, and if there are no problems, only that translation check is required. However, if there are omissions or mistranslations, the MT result is used to make corrections. The machine-translated text is corrected to the required level of accuracy, by either “full post-editing,” which is a fluent and accurate translation with background information, or “light post-editing,” which is a simplified post-editing process involving some reworking to get the gist of the translation.
Translation, on the other hand, is the process of rewriting two different background languages in another language. The text is translated not only to make it more readable and natural, but also to reflect the cultural background in the content of the translation.
The difference between post-editing and translation can be seen not only as a difference in work, but also as a difference in translation result. In post-editing, the priority is to be semantically correct, because the focus is on working time.
In translation, on the other hand, the emphasis is on content. It is characterized by paying greater attention to readability than in post-editing, whether the translation has the tone required for the content, and whether it reflects the cultural background and context.
■Role of Post-editing and Machine Translation
The rise of post-editing has been fueled by the recent explosion of MT tools and improvements in accuracy. The accuracy of AI translation tools has dramatically improved, but at this point they are still no match for human translation. That is why post-editing is necessary.
With the globalization of business, translation opportunities are increasing and so are translation volumes. This creates problems, such as the inability to handle translation tasks that could previously be handled in-house, and the excessive time and budget required for translations.
The advantage of MT is speedy translation. However, in many cases, the accuracy of translation results is not as good as human translation. Therefore, post-editing is now used after MT to address the problem of translation accuracy.
The role of translation is to convey a message. Even if MT is used, the message to be conveyed can be conveyed by taking the extra step of post-editing.
■Post-editing and Pre-editing
A similar term to post-editing is “pre-editing.”
Both processes are done by a human editor to improve the output of machine translation methods.
They differ in that post-editing is when corrections are applied to a machine-translated output, whereas pre-editing is when texts are checked for things that machine translation can struggle with and edited for clarity before they are translated. This can mean things like shortening longer sentences or avoiding double negatives, or reviewing the context or other materials to ensure that grammatical elements essential for easy understanding are present.
Using both the pre- and post-editing processes can not only raise the quality of machine-translated output but get it done quicker too.
■Necessary Post-editing Skills
High-quality post-editing demands many skills from a translator, from understanding a text’s background, reading between the lines and rendering nuances into natural expressions, to information gathering, research and specialized knowledge.
A translator must also be careful not to add information that is not found in the source or leave out vital information from it, and also be able to identify the kinds of errors that are typical of machine translation.
The ISO 18587 international standard for post-editing is granted to businesses that provide post-editing services that strictly adhere to established guidelines and meet a high standard of quality. Since there is no organization in Japan that supports companies who wish to acquire this certification, companies can evaluate their own compliance with the standards and, if applicable, can operate and declare their compliance with the standards at their own responsibility. This “supplier’s declaration of conformity” system is defined by ISO/IEC 17050 (JIS Q 17050).
When choosing a translation company for post-editing, consider choosing one that has declared compliance with ISO 18587.
■The Advantages of Post-Editing
The dramatic development of AI translation is behind the increased demand for post-editing, which is the process of improving the accuracy of texts translated by machine translation. A major merit of AI translation is the ability to translate a large volume of text in a short amount of time. If the translation output is highly accurate, there are cases where extensive post-editing may not be necessary, which greatly reduces time spent translating. Even with light post-editing, where the goal is to make the broad idea of a translation understood, post-editing can be kept to a minimum, reducing the time needed to complete the translation.
Thus, the advantage of post-editing is clear: the amount of time spent translating can be reduced by combining post-editing with highly accurate machine translation like AI translation.
■Points for Using and Requesting Post-editing
The number of users of readily available MT tools is growing every year due to reasons such as the fact that human translation takes too much time. MT is speedy and convenient, but in some cases, translation accuracy may be insufficient depending on the translation tool. In such cases, if post-editing is performed to improve accuracy, depending on the accuracy of the original MT results, the entire document may have to be re-translated, resulting in a situation where the total time required for translation is the same as that required for human translation. Therefore, the use of highly accurate MT tools is important to reduce the time required for post-editing.
Post-editing tends to be less accurate than human translation, but if a certain level of quality is required, there are ways to improve the accuracy of MT results by performing pre-editing as well as post-editing after machine translation, including AI translation. Pre-editing, which eliminates the incomprehensibility and ambiguity of the source text, improves the accuracy of MT results by taking the time to provide the subject and shorten long sentences. As a result, the time required for post-editing is reduced.
When requesting post-editing, the presence or absence of ISO 18587 certification, the international standard for post-editing, is also a criterion for judging the quality of post-editing.
■Things to Be Aware of When Requesting Post-Editing
When doing post-editing, it’s important to understand the level of quality that is required for the deliverable, which will help you distinguish whether you will need full post-editing or light post-editing to ensure that the finished translation meets the required standards.
Choosing between full post-editing or light post-editing depends on the desired translation accuracy and the amount of time spent translating. Full post-editing requires a high degree of translation accuracy, but if the requirement is too high, it may take just as long as a human translator. Spending a lot of time post-editing negates the biggest benefit of machine translation, which is saving time. That’s why it’s best to determine whether to use full post-editing or light post-editing depending on the content and deadline, use highly accurate machine translation tools, and commission a translation company that can perform high-quality post-editing.
■Toin’s Post-editing
At Toin, our highly experienced post-editors have advanced translation skills and knowledge about light post-editing and full post-editing and can quickly optimize machine-translated text according to your needs. T-tact AN-ZIN, Toin’s AI translation tool, is also available.
ISO 18587 certified
Toin has made a supplier’s declaration of conformity with ISO 18587, the international standard for post-editing, since December 1, 2022. With our high-quality full post-editing service, we provide AI translations that are highly accurate and reliable.
Highly skilled translations
Toin has obtained ISO 17100 certification in the fields of “information technology and telecommunications,” “medicine and pharmaceuticals,” and “finance, economics and law.” We support your translation work by translators providing high-quality translations performed by expert and backed by international standards, helping you to streamline your business.
Types of post-editing
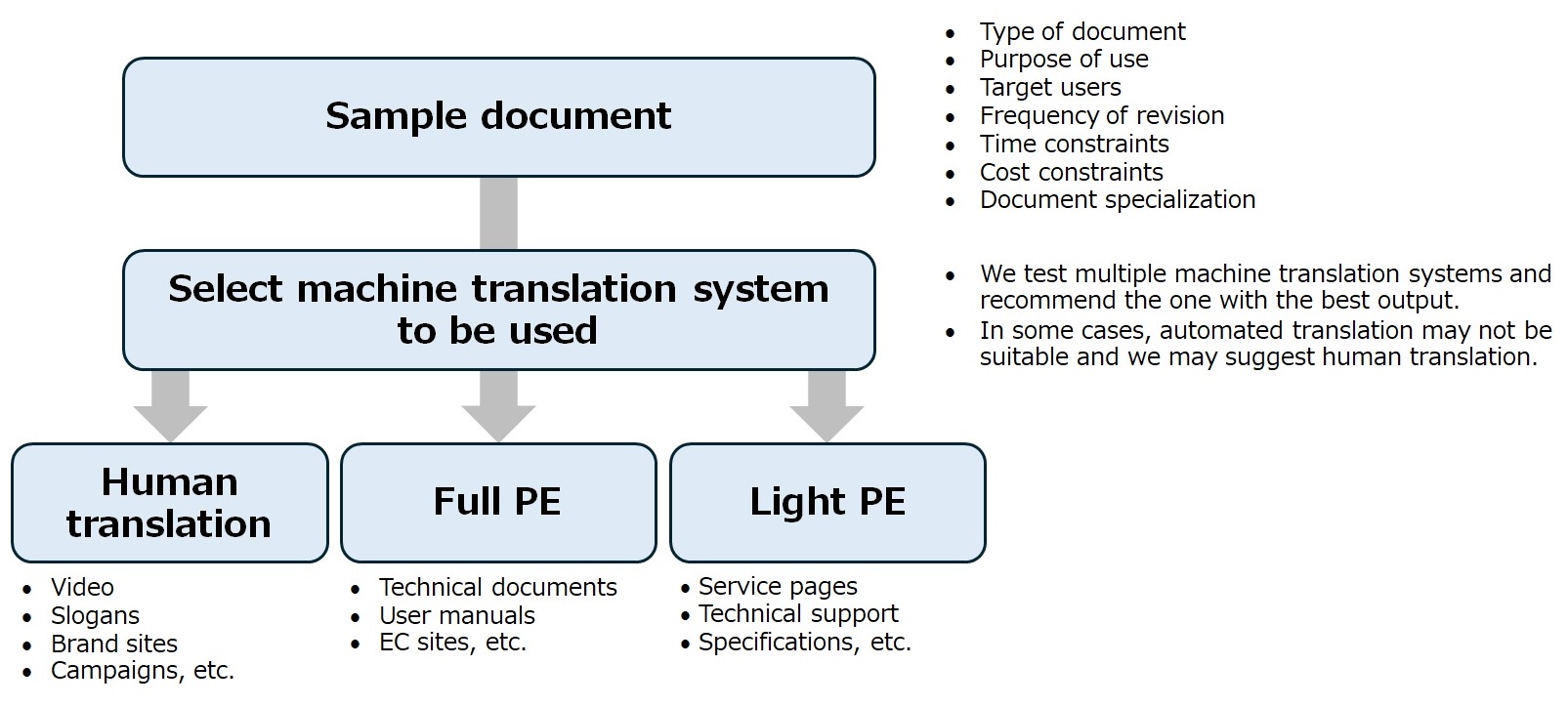
There are two types of post-editing: full post-editing, where we finish the document to the same level of quality as a human translation, and light post-editing, where we only touch up the content so it’s understandable. If you provide us with a sample document, we can propose the best MTPE flow for you, considering your intended use, frequency of revision, and time and cost constraints.
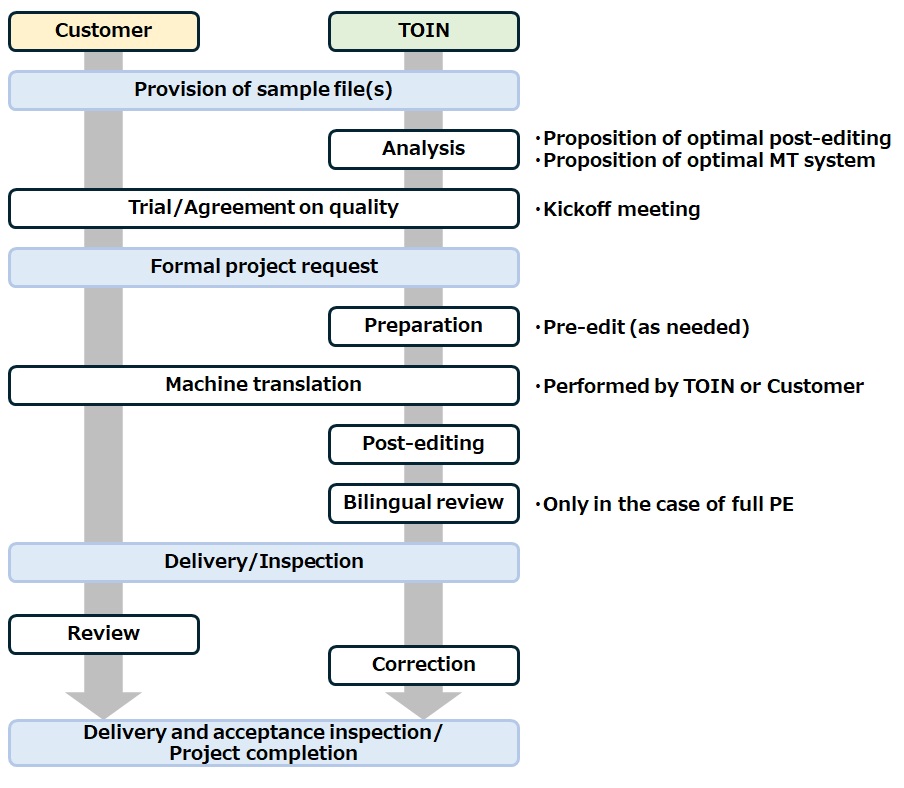
We provide safe, high-quality and professional total translation services that only a translation company with a long history can offer, including post-editing, human translation and AI translation. If you are considering implementing a high-quality post-editing service, please feel free to contact us at Toin.
See here for information on Toin’s AI translation service T-tact AN-ZIN®.








